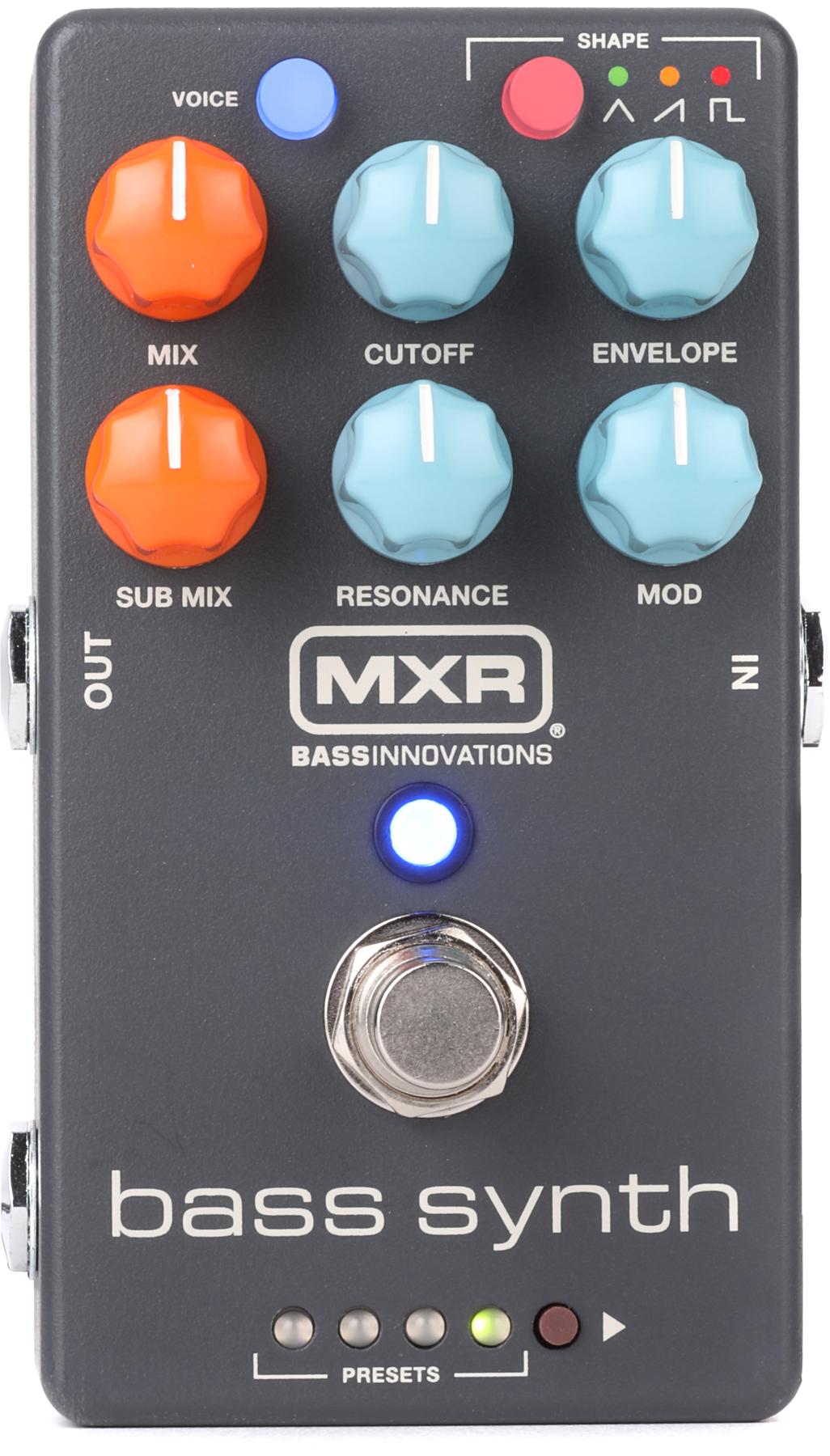
Kevin Shields tone chasers are a minor cult—sharing insights and discoveries about ways and means to replicate the intoxicating, enveloping sounds of My Bloody Valentine’s LPs, and in particular, their masterwork, Loveless. It’s a curious pursuit, in a way, for it is well documented that Shields created most of that album’s time- and space-bending sheets-of-sound guitar parts via the rather economical combination of reverse reverb and the vibrato on a Fender Jazzmaster.
My Bloody Valentine on stage, however, is quite another matter. Seeing the band live is a little like breathing the atmosphere of another planet. It’s heavy, loud, and sometimes disorienting, which is largely the product of a sea of colliding and intertwining overtones. It’s an almost extra-dimensional extension of the songs on the records. And to build the melodious, swirling, and deafening world of MBV live, Shields relies on an imposing quiver of stompboxes. As it turns out, one of the most critical of these is a vintage Fender Blender, an octave fuzz that went largely unappreciated in its time. With the release of the Fender Shields Blender, a highly modified version of the original, the Blender’s days in the shadows are likely numbered.
Building on a Blend
For those less familiar with Shields’ work, it’s important to know that his ears, mind, and aesthetic fixations dwell, to a significant extent, in the realm of overtones, and the magic made when they interweave to form a more colorful whole. Curiously, one of Shields’ and My Bloody Valentine’s deepest probes into the overtone world is the bludgeoningly loud and sustained onslaught of the song “You Made Me Realise.” Shields’ first investigations of the Blender’s potential occurred during this nightly, set-ending ritual. And the combination of octave-up fuzz, a footswitchable fuzz boost, a tone knob, and a wet/dry blend control made it a perfect vehicle for adding another color to the song’s outro overtone feast. The Shields Blender, however, explodes and expands the feature set—and the available sounds—of the original Blender significantly.
Bigger Blend, Minds Blown
Shields’ and Fender’s design additions profoundly expand the possibilities afforded by the new Blender. First, there’s a new footswitchable, mammoth sub-octave fuzz with dedicated volume control. It can be used with or without the octave up signal from the original, which can now be added or subtracted via a pushbutton. That means you can use the fuzz alone, with one of the octave effects, or both. That flexibility gives you a wagonload of huge, menacing, and mangled textures to work with. But they are just a fraction of the tones you can craft here. The fuzz has its own very range-ful tone knob, which recasts the fuzz’s personality considerably. The expand section, which has a dedicated footswitch (and was called the tone boost on the original) enables you to boost the fuzz output.
The wildest addition to the original Blender, though, is the sag circuit. Shields noted that many sag functions, which starve a circuit of voltage, are a bit subtle. This one is most assuredly not. It’s also not the easiest function to figure out. But practice yields very cool and often unexpected results. While it works in dynamically responsive, rhythmic, almost tremolo-like ways at the right settings (which seems to be Shields’ preferred application), I loved its potential in fingerpicked situations, where its dynamic responsiveness shined. Fingerpicking triads high on the neck with both octave effects engaged yielded melodic, glitchy effects that could be continuously reshaped by touch, and by using mellower trigger levels you can summon a greater degree of dynamic control. It’s important to note that strong octave-down fuzz settings can render the sag control less nuanced. But used together they can also summon the chaotic, tectonic-scale, Earth-cracking tonalities that are part of the live “You Made Me Realise” or Neil Young’s most deranged octave divider and melting tweed Deluxe moments.
The Verdict
While it yields many chaotic results, the Fender Shields Blender is not the product of a chaotic design approach. Shields is known for striving for very specific sonic results and for being uncompromising in those quests. That a Kevin Shields-approved pedal could exist at all is something of a surprise to this longtime fan. But what’s also a surprise is how incredibly varied and full of twists the Shields Blender can be. The addition of the sub-octave fuzz is inspired. So is the tricky-to-wrangle, but ultimately satisfying, sag circuit, which offers unusual tones and interactivity galore. Making the fuzz independently operable from the octave effects also extends the pedal’s flexibility. But it’s the potential interrelationships between all of the controls and functions that ultimately make the Shields Blender such a rich mine of possible sounds. For the intrepid and patient explorer willing to crack the many codes within, fantastic rewards await.